Spans - Individual Operations
Understanding spans and how they represent individual operations within traces
A span represents a single operation within a trace. It's the building block that makes up the complete request journey. Each span has a start time, end time, and can contain child spans, creating a hierarchical structure.
🎯 What is a Span?
A span represents:
- A single function call or method execution
- An LLM API call to a specific model
- A database query or external API call
- A business logic operation like data processing
- A tool execution in an agent workflow
🏗️ Span Structure
Every span contains:
- Span ID: Unique identifier within the trace
- Trace ID: Reference to the trace it belongs to
- Name: Descriptive name of the operation
- Start/End Time: When the operation began and completed
- Duration: How long the operation took
- Status: Success, error, or other completion state
- Attributes: Key-value metadata
- Events: Point-in-time occurrences
- Child Spans: Nested operations
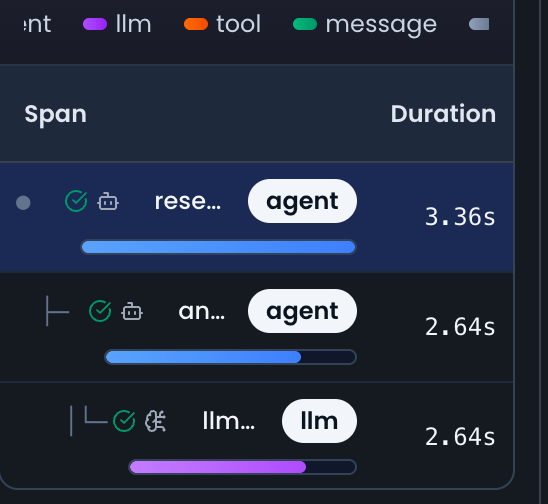
📊 Visual Hierarchy
Here's how spans form a hierarchical structure:
🔄 Span Lifecycle
1. Span Creation
2. Add Attributes
3. Add Events
4. Set Status
🎯 Span Types in AI Applications
LLM Spans
Agent Spans
Tool Spans
Custom Operation Spans
📈 Span Attributes
System Attributes
AI-Specific Attributes
Business Attributes
🎪 Span Events
Operation Events
AI Events
Error Events
🔍 Span Analysis
Performance Metrics
- Duration: How long the operation took
- Latency: Time spent waiting for external services
- Throughput: Operations per second
- Resource Usage: CPU, memory, network usage
Error Analysis
- Error Rate: Percentage of failed operations
- Error Types: Common failure patterns
- Retry Patterns: How often operations are retried
- Recovery Time: Time to recover from errors
Cost Analysis
- Token Usage: Input and output tokens
- API Costs: Cost per operation
- Resource Costs: Infrastructure costs
- Total Cost: End-to-end operation cost
🔗 Parent-Child Relationships
Creating Child Spans
Span Context
🚀 Next Steps
Now that you understand spans, explore these related concepts:
- Traces - Complete request journeys
- Attributes - Metadata and context
- Events - Point-in-time occurrences
Best Practices
- Spans Best Practices - Learn how to create effective spans
Spans are the building blocks of observability. They provide detailed insights into individual operations, making it easy to understand performance, debug issues, and optimize your AI applications.
Get Early Access to Noveum.ai Platform
Be the first one to get notified when we open Noveum Platform to more users. All users get access to Observability suite for free, early users get free eval jobs and premium support for the first year.